![]()
XML
XML 是一种可扩展的数据标记语言,被用于传输数据
基本语法
- XML 的标签为自定义标签,标签必须成对
- XML 结构为树结构,需要有一个根标签,通常具有头声明
- xml 属性必须用引号包围,单引号或双引号都可以,若属性值包含双引号,则可以用单引号包围属性值,或者使用实体引用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<root>
<name></name>
<author></author>
<msg>
<price></price>
</msg>
</root>
|
常用实体引用
| < |
< |
小于 |
| > |
> |
大于 |
| & |
& |
和号 |
| ' |
’ |
单引号 |
| " |
" |
引号 |
xml 的样式表语言为 XSLT,也可使用 css 设置样式
样式链接声明:<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="simple.xsl"?>
命名空间
用于解决不同 xml 文档中相同标签的冲突
-
使用前缀解决冲突:<h:table></h:table>
-
使用默认命名空间
在冲突标签中加入 xmlns 属性,<table xmlns="namespaceURL"></table>
-
使用前缀 + 命名空间
在冲突标签中加入前缀和 xmlns 属性,<h:table xmlns:h="namespaceURL"></h:table>
CDATA 标签
当标签内使用大量不需要解析的字符,如使用大量实体引用或代码,可以使用 CDATA 标签
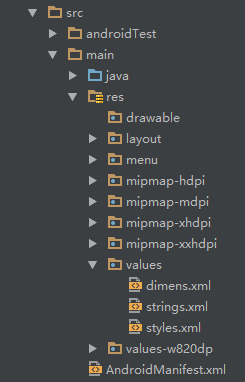
工程项目结构
使用 Android Studio 创建 Android 工程得到如下项目结构
编程时主要使用 java 和 res 两个文件夹
- java: 业务代码存放的地方
- res: 存放资源文件的地方,如图片,音频,动画和其他 xml 文件
资源文件
资源文件放在 res 文件夹中
- drawable:存放各种位图文件,(.png,.jpg,.9png,.gif 等) 除此之外可能是一些其他的 drawable 类型的 XML 文件
- mipmap-hdpi:高分辨率,一般我们把图片丢这里
- mipmap-mdpi:中等分辨率,很少,除非兼容的的手机很旧
- mipmap-xhdpi:超高分辨率,手机屏幕材质越来越好,以后估计会慢慢往这里过渡
- mipmap-xxhdpi:超超高分辨率,这个在高端机上有所体现
- layout:该目录存放布局文件
- values 目录
- demens.xml:定义尺寸资源
- string.xml:定义字符串资源,在代码中通过 R.string.string_name 或者在 xml 中通过@string/string_name 获取
- styles.xml:定义样式资源
- colors.xml:定义颜色资源
- arrays.xml:定义数组资源
- attrs.xml:自定义控件时用的较多,自定义控件的属性!
- theme 主题文件,和 styles 很相似,但是会对整个应用中的 Actvitiy 或指定 Activity 起作用,一般是改变窗口外观的,可在 Java 代码中通过 setTheme 使用,或者在 Androidmanifest.xml 中为<application…>添加 theme 的属性
- raw 目录:存放音频视频等
- 动画
- animator:存放属性动画的 XML 文件
- anim:存放补间动画的 XML 文件
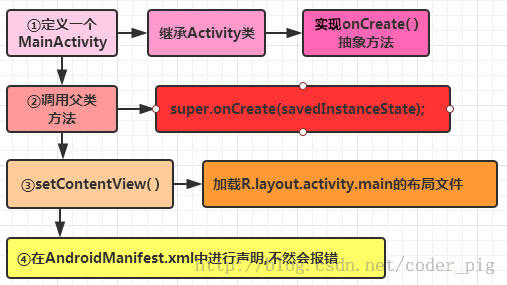
三大文件解析
-
MainActivity.java:程序的主页面,可在 AndroidManifest.xml 中修改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| package jay.com.example.firstapp;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
|
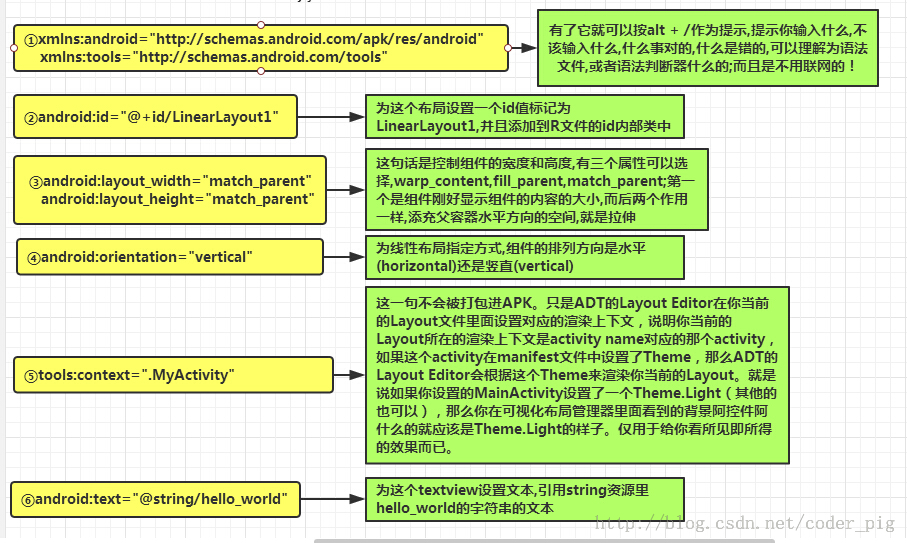
-
activity_main.xml:MainActivity.java 对应的布局文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
</LinearLayout>
|
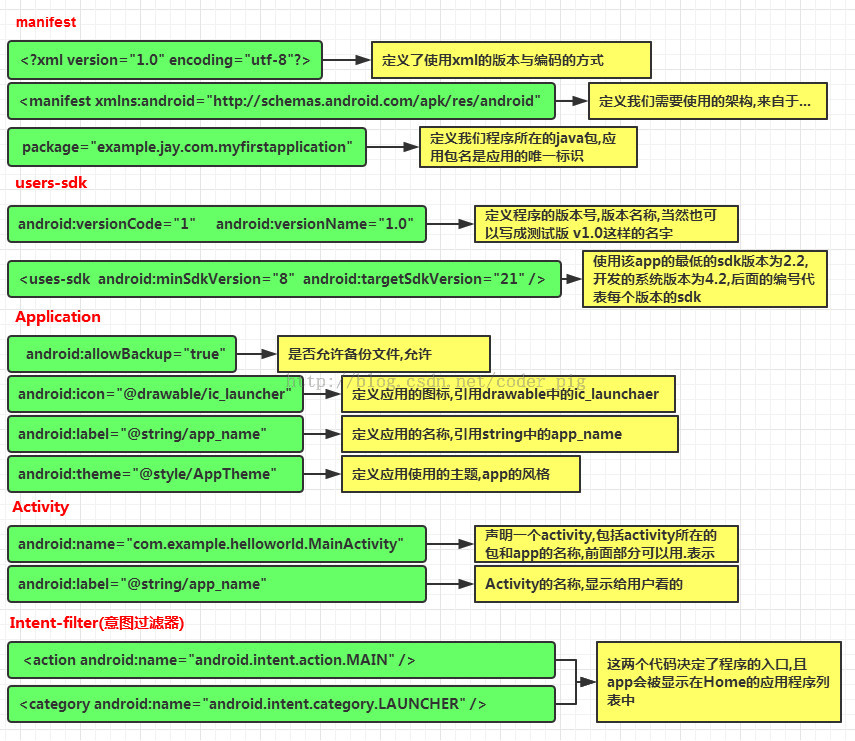
-
AndroidManifest.xml:Android 项目的主配置文件,可配置应用所用的 Activity、Service、Broadcast 和 ContentProvider,以及声明权限
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="jay.com.example.firstapp" >
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
|